Incapacity for work always raises complex questions in Payroll: How long does continued pay apply? When can holidays be reduced? What happens to pension fund contributions and family allowances? This article provides a compact overview and practical tips for legally compliant implementation.
What HR needs to know
When employees are absent due to illness or accident, a challenging phase begins for Human Resources. In addition to the emotional burden for those affected, numerous legal and administrative questions arise. Transparent communication is crucial, especially for longer absences. HR should provide information about possible consequences such as salary, holidays, pension fund and allowances at an early stage. An information sheet or a brief discussion can reduce uncertainty and build trust and should therefore always be to hand. Possible components of such a leaflet are shown in the following text. It should include the insurance company's contact details, policy numbers and any supplementary insurance services. In addition, the regulations in the staff regulations and any collective labour agreement (CLA) must always be taken into account.
Continued payment of salary: Who pays and when?
Illness:According to Art. 324a CO, employees are entitled to continued payment of salary - depending on years of service and regional scale. If you have voluntary daily sickness allowance insurance (KTGV), this often covers up to 730 days within a 900-day period. The number of days of absence is added up per year of service and paid out up to the maximum regulated period of entitlement. A new entitlement arises at the change of year of service, provided the absence does not extend beyond the change of year of service.
Accident: The compulsory accident insurance pays 80% of the insured salary from the third day after two days of waiting at the employer's expense. The accident day is to be paid as a normal pay day and not treated as a day of absence. Voluntary supplementary accident insurance can pay for insurance benefits that are not already covered by the compulsory accident insurance, such as the 20 % additional salary payment or additional outpatient or inpatient services.
In the event of partial incapacity for work, the duration of the entitlement to continued salary payment must be extended proportionately in accordance with the Swiss Code of Obligations and the scale. In concrete terms, this means that three weeks' continued salary payment in the event of 100 % incapacity for work corresponds to six weeks' continued salary payment in the event of continuous incapacity for work of 50 %.
Please note: With the annual salary method, the salary reduction of the 13th month's salary is already taken into account and must be paid out in full. This must be checked in the settings of the payroll system.
Net salary compensation: yes or no?
Daily sickness and accident benefits are not subject to social insurance contributions. This means that the net salary can be higher than the regular salary payment. The so-called net salary compensation is not conclusively regulated by law - employers who continue to pay full salary during the period of incapacity for work can apply the net salary compensation, provided that it is clearly stated in the employment contract. The net salary equalisation offsets the reduced social insurance contributions and avoids the salary payment being higher than if the employee were healthy. The offsetting of this difference is also subject to social insurance contributions. This is done to avoid creating false incentives to prolong incapacity for work.
If the system is maintained correctly, the net salary corresponds to the net salary before the incapacity for work. In the event of a salary reduction, however, net salary compensation should be deactivated, as otherwise the employee would be paid less than the 80 %. The procedure for net salary equalisation often raises questions among employees. It should therefore definitely be included in the information sheet.
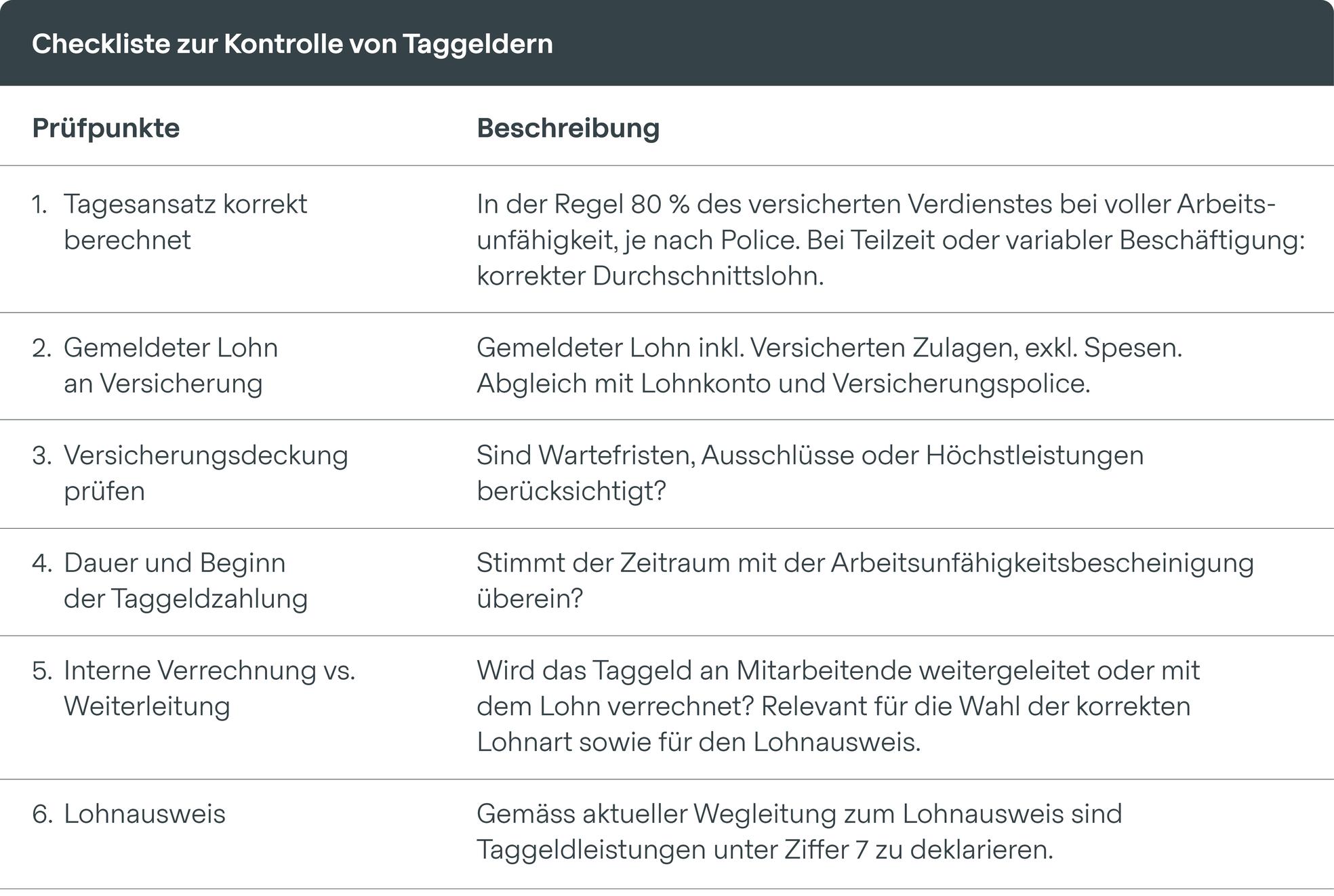
Checking daily allowances
The salary reported to the Insurances must be correct, as it forms the basis for calculating the daily allowance. Incorrectly reported insured earnings can lead to incorrect daily allowance rates and reclaims or to a small daily allowance. It is advisable to read the insurance policies and the General Terms and Conditions of Contract (GTC) to find out exactly which salary components are to be taken into account in the event of a benefit, and to adjust and reconcile the systems accordingly. Insured persons are entitled to irregularly paid salary components if the employer would otherwise be unjustly enriched. Specifically, this includes, for example, inducements or bonus payments if contributions have been paid on these.
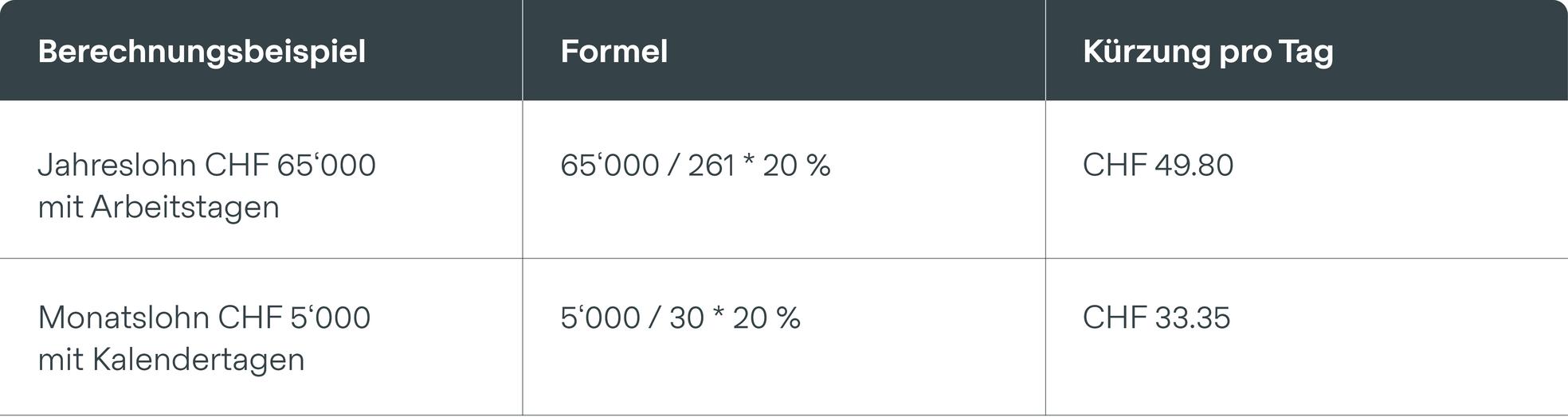
Holiday reduction for long-term absence
According to Art. 329b CO, holiday entitlement may be reduced by 1/12 per month from the second full month of incapacity for work through no fault of the employee.
Exceptions:
- Pregnancy: 2 full months grace period
- Maternity leave (14 weeks): no reduction
It should be noted that, for practical reasons, a full month of absence is always deemed to exist as soon as an employee is unable to work for 21.75 days.
What else needs to be considered?
BVG premium exemption
Many pension funds exempt policyholders from the obligation to pay contributions after three months. The insurance remains in force and the savings contributions continue to be credited to the pension fund.
Family allowances
The entitlement remains in force for the current month and the following three months after the start of the period of incapacity for work. Thereafter, the other parent must apply for the allowances. If the other parent is not entitled, an application can be made for family allowances for non-employed persons. Upon resumption of employment, the entitlement applies from a monthly income subject to AHV contributions of CHF 630.
AHVcontributions when receiving daily allowances
Daily allowances exempt from social security contributions may result in AHV gaps in the insured person's individual account. Employers should check whether the minimum annual AHV contribution of CHF 530 has been paid for their employees in accordance with the statutory requirements in order to avoid gaps in contributions and the resulting pension losses. In such cases, employees can submit the "Registration for non-employed persons" form to their compensation office.
Key takeaways
- Contractual clarity: set out regulations on net salary compensation in writing
- Check salary systems: Correctly map BVG deductions and daily allowance settlements
- Ensure communication: Inform employees about AHV contributions in relation to family allowances and pension fund contributions
- Check daily allowances: Carefully check payment and settlement
Author

Denise Bättig
HR Services
Denise is a Payroll Expert and social insurance specialist at HR Campus. She provides practical support to companies in the optimisation of HR and Payroll processes - especially where legal requirements and payroll systems come together.
HR Knowledge
In our download portal you will find useful fact sheets, helpful checklists and supporting information for you and your HR team to download.
